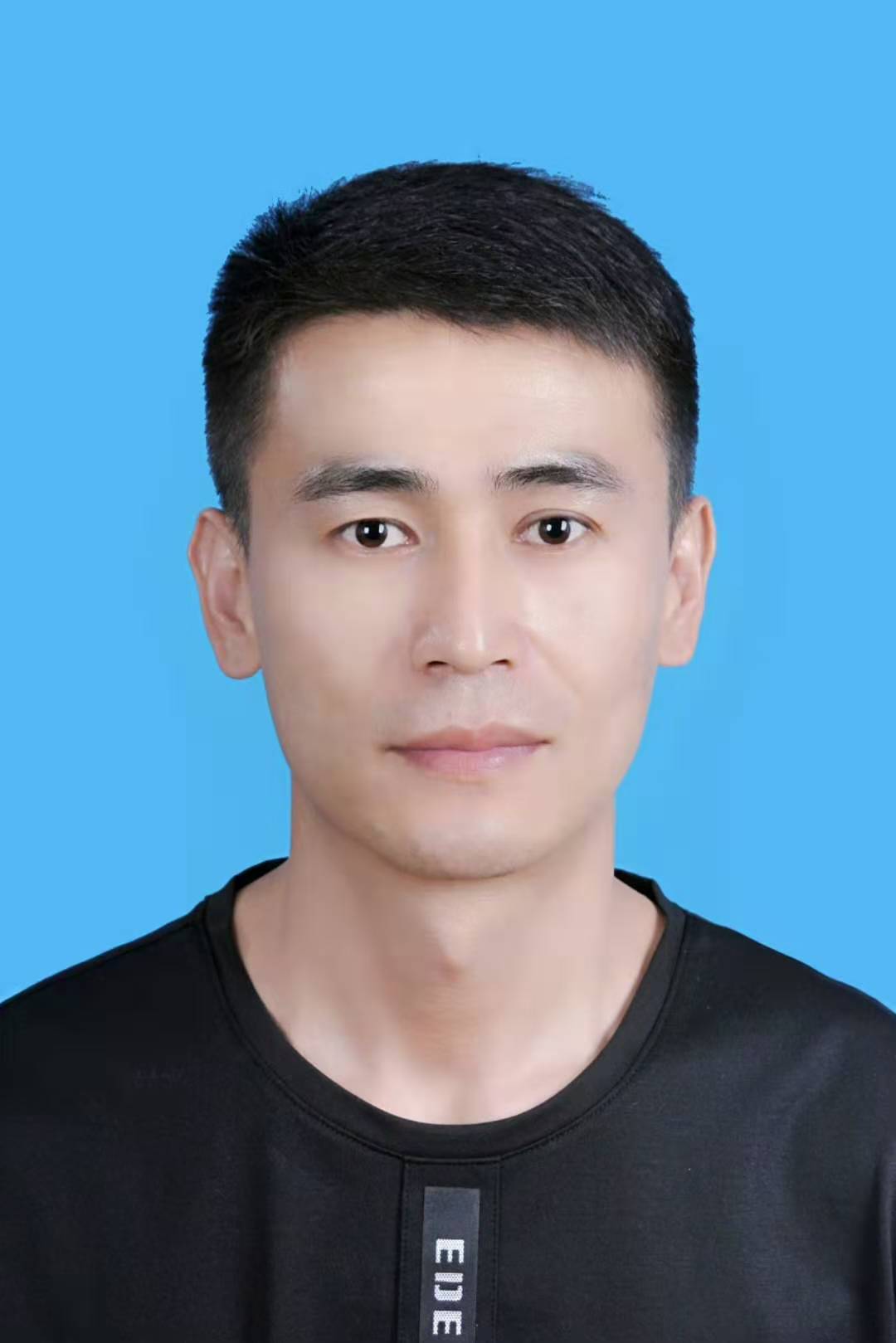
Haiyun Li, male, Sep 1989, Doctor, Researcher
E-mail:lihaiyun@lzu.edu.cn
Research Directions
Microbial ecology of grassland;Microbial soil remediation
Education
2016.09-2019.12 Gansu Agricultural University, Pratacultural Science, Doctor
2012.09-2015.06 Northwest Normal University, Microbiology, Master
2008.09-2012.06 Hexi University, Biological Engineering, Bachelor
Work Experiences
2020.08-Now Collaborative Innovation Center for Western Ecological Safety, Lanzhou University, Early-Career Researcher
Academic Part-time Job
Member of the Grassland Ecology Professional Committee of the Chinese Grassland Society; reviewer for the journals "Plant and Soil", "Journal of Soil and Water Conservation" and "Journal of Applied and Environmental Ecology"
Research Experiences
1. "Double First-Class" Special Guidance Project-Team Building Funds-Research Startup Fee (561120202), Sep 2020-Aug 2025, 1 million yuan, in research, presided over
2. National Natural Science Foundation of China: Interaction mechanism of "soil - plant –microbes" of degradated grassland in east Qilian alpine region (31660688), 2017.01-2020.12, 390,000 yuan, in research, Participate, (2/9)
Academic Publications
1. Haiyun Li, Yizhi Qiu, Tuo Yao, et al. Evaluation of seven chemical pesticides by mixed microbial culture (PCS-1): degradation ability, microbial community, and Medicago sativa phytotoxicity[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 389: 121834.
2. Haiyun Li, Yizhi Qiu, Tuo Yao, et al. Effects of PGPR microbial inoculants on the growth and soil properties of Avena sativa, Medicago sativa, and Cucumis sativus seedlings[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2020, 199: 104577.
3. Changning Li, Haiyun Li, Tuo Yao, et al. Effects of microbial inoculation on enzyme activity, available nitrogen content, and bacterial succession during pig manure composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 306: 123167.
4. Changning Li, Haiyun Li, Tuo Yao, et al. Microbial inoculation influences bacterial community succession and physicochemical characteristics during pig manure composting with corn straw[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 289: 121653.